Wisdom Tooth Extraction:
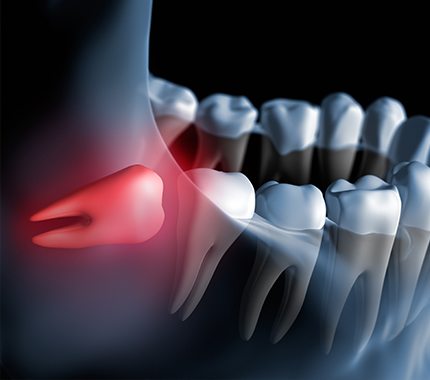
Wisdom teeth or third molars are the last permanent teeth to appear in the oral cavity. These usually erupt between the ages of 17 to 25 and are known to cause problems for many due to a lack of space in the jaw. If the tooth doesn't have room to grow (impacted wisdom tooth), it might result in pain, infection, or other dental problems, and you'll likely need to have it pulled.
To prevent potential problems, your dentist might recommend wisdom tooth extraction even if the impacted wisdom teeth aren't currently causing problems. Usually, the procedure is carried out under local anesthesia and if stitches are placed, the stitches will be taken out within a week.
Relieves Pain
Prevents Damage to Adjacent Tooth
Prevents Infection
What is Tooth extraction?
Tooth extraction is the removal of a tooth from its socket without causing any damage to the surrounding supportive tissues.
The pain of tooth extraction procedures varies depending on the tooth's eruption into the oral cavity.
Types of Tooth Extraction
There are two types of tooth extraction: simple extraction and surgical extraction.
1. Simple extraction:
A simple extraction is performed on a tooth that is visible in the mouth and is above the gum line. These teeth are usually easily removed by loosening the tooth with an elevator and pulling it out with forceps.
2. Surgical extraction:
A surgical extraction is performed on a tooth that is below the gum line or is completely embedded in the bone. These teeth are impacted.
Reasons for tooth extraction:
- Decayed tooth
- Impacted/ Infected Wisdom tooth
- Retained Milk teeth
- Periodontal problems
- In Prosthesis
Who needs wisdom tooth extraction:
- Wisdom teeth are typically extracted only if they are causing or are likely to cause problems in the future.
- When there is pain or stiffness in the jaw. Redness and swelling in the jaw are the symptoms that you need to extract your wisdom tooth.
- Wisdom teeth can become trapped or impacted within the jaw, resulting in infection or abscess that damages the roots of other teeth and erodes bone support.
- Erupting partially through the gums, but difficult to see and clean, this serves as a breeding ground for bacteria that cause gum disease and oral infection.
- Erupting fully, but causing crowding and damage to otherwise healthy surrounding teeth by growing at an angle.
Procedure of wisdom tooth extraction:
- To expose the tooth and bone, an incision is made in the gum tissue.
- The bone that is impeding access to the tooth root is removed.
- If it is easier to remove the tooth in sections, it is divided into sections.
- Any debris from the tooth or bone at the site of the extracted tooth is removed.
- The incised gum tissues are then sutured.
- These sutures will be removed in a few days.
Consequences of Not Getting Wisdom Teeth Removed:
- Because your permanent teeth are already in place, the eruption of this extra set of molars may cause them to shift. This causes pain, bite problems, and overcrowding making brushing and flossing difficult and eventually leading to cavities or tooth decay.
- Wisdom teeth can cause damage to the jawbones, affecting the function and motion of the mouth.
- We all know that the mouth and nose are closely linked, but did you know that impacted wisdom teeth can have an impact on the sinuses? When the growth of these molars causes sinus pain, pressure, and congestion, wisdom teeth extraction is recommended.
- Wisdom teeth that erupt at an angle to the other teeth or horizontally can cause the gums to swell and make cleaning difficult. These reddish areas along the gum line are often sensitive to touch, preventing proper brushing and flossing and ultimately leading to cavities and tooth decay.
Frequently Asked Questions
Answer: It is determined by the complexities of your case. However, most people return to normalcy within a few days. You should be able to resume normal activities within 48 hours.



